Balancing Poll
Should peace keeping be led by regional organizations (1) or should the United Nations (UN) have its own permanent military force instead of relying on member states (2)?
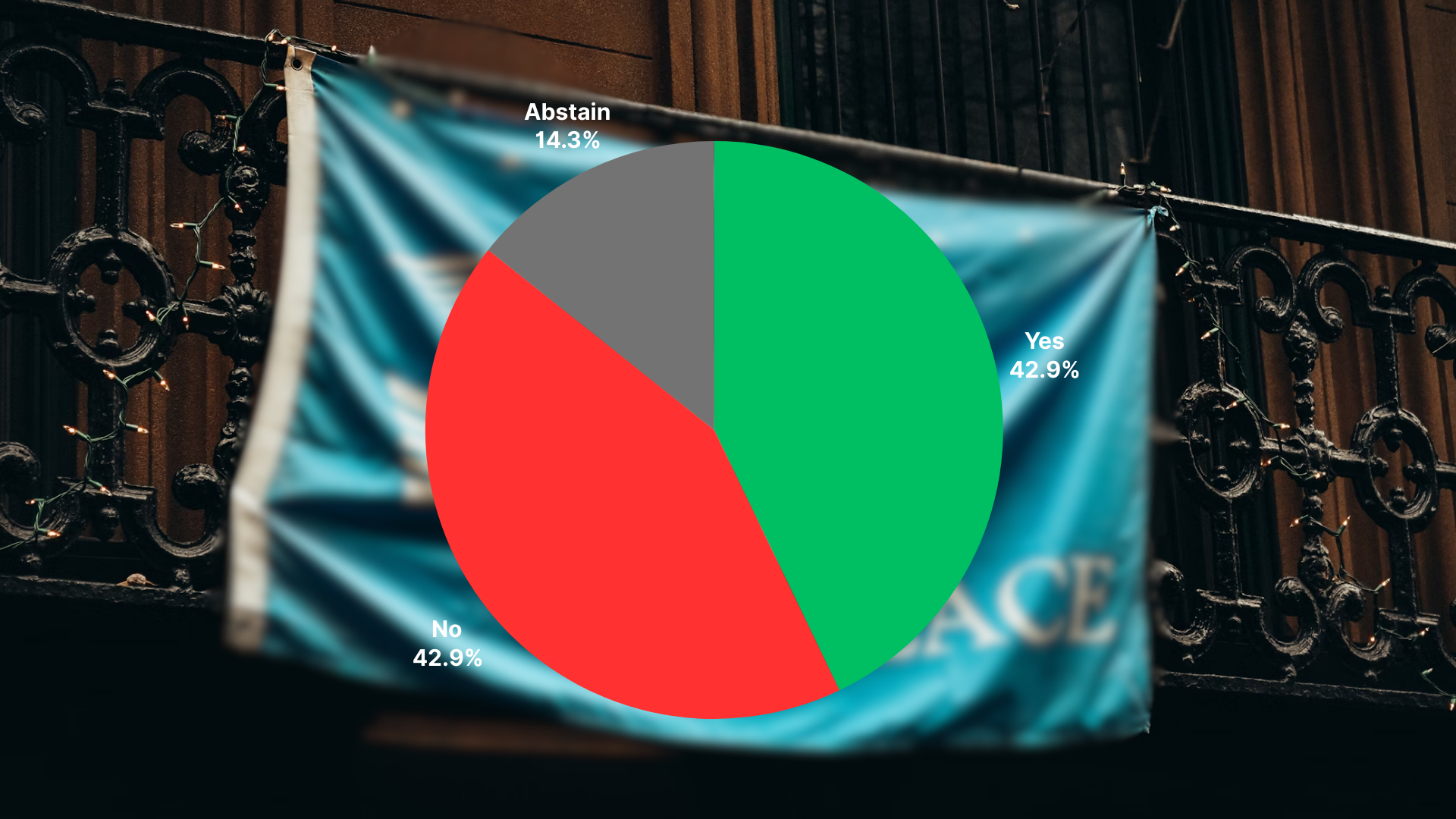
The above opinion poll illustrates the sharp divide between regional interference and UN led military force. While 42.85% of the committee prioritized regional-led peacekeeping, advocating for localized solutions, an equal 42.85% emphasized global coordination by supporting a permanent UN force, while the United States of America (USA) abstained from voting completely.
The USA’s abstention, though silent, was telling- it reflected a strategic reluctance to commit. This reinforces their evasive stance in the situation which is particularly controversial given their extensive funding of UN peace keeping missions. Additionally, the USA has favored ad-hoc coalitions that allow them to maintain flexibility without being bound by constraints. For example, The Biden Administration created partnerships such as Quadrilateral Security Dialogue show how the USA builds partnerships to advance its own interests. Thus, their abstention not only shows non commitment but also a favoring of flexible, issue-based coalitions over a permanent UN force.
The Republic of France’s strong advocation for multilateralism explains their voting stance. They have actively promoted resolutions of the UNSC, including the addition of permanent and non-permanent seats to increase the recognition of the UN. However, the Republic of India’s voting stance complicates matters. They have stressed the importance of sovereignty and consensual humanitarian intervention. Supporting a UN military force goes against its past reluctance for foreign intervention in its region.
The Russian Federation’s skepticism of Western-led interventions supports their vote. Furthermore, their focus on strengthening of the Collective Security Treaty Organization presents an alternative to a Western-led army. Similarly, the People’s Republic of China and Japan’s support is substantiated by their emphasis on their own regional organizations and a more decentralized UN structure.
